
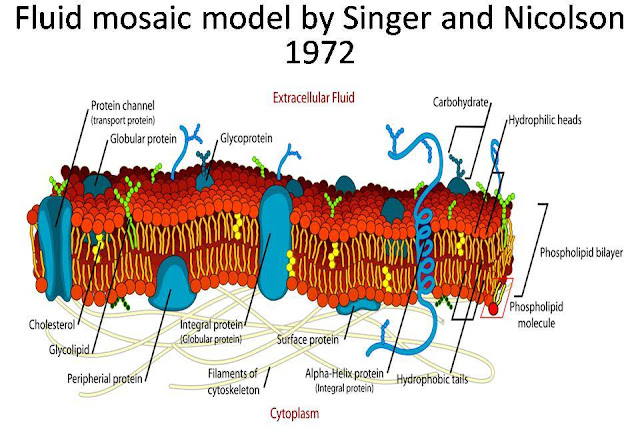

A phospholipid molecule consists of a three-carbon glycerol backbone with two fatty acid molecules attached to carbons 1 and 2, and a phosphate-containing group attached to the third carbon. Hydrophobic, or water-hating molecules, tend to be non- polar. The hydrophilic or water-loving areas of these molecules are in contact with the aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell. The main fabric of the membrane is composed of amphiphilic or dual-loving, phospholipid molecules. Carbohydrates attached to lipids (glycolipids) and to proteins (glycoproteins) extend from the outward-facing surface of the membrane. The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane: The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. The principal components of a plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates attached to some of the lipids and some of the proteins. Generally attached to outside of membrane layer On the inner or outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer not embedded within the phospholipidsĬarbohydrates (components of glycoproteins and glycolipids) May or may not penetrate through both layers. Integral proteins (for example, integrins)Įmbedded within the phospholipid layer(s). Components of the Plasma MembraneĪttached between phospholipids and between the two phospholipid layers The mitochondrial inner membrane contains 76% protein and 24% lipid. For example, myelin contains 18% protein and 76% lipid. The proportions of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in the plasma membrane vary with cell type. For comparison, human red blood cells, visible via light microscopy, are approximately 8 µm wide, or approximately 1,000 times wider than a plasma membrane. Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness. The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components -including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates-that gives the membrane a fluid character. The model has evolved somewhat over time, but it still best accounts for the structure and functions of the plasma membrane as we now understand them. Nicolson in 1972 to explain the structure of the plasma membrane. The fluid mosaic model was first proposed by S.J. hydrophobic: Lacking an affinity for water unable to absorb, or be wetted by water,”water-fearing.”.hydrophilic: Having an affinity for water able to absorb, or be wetted by water,”water-loving.”.amphiphilic: Having one surface consisting of hydrophilic amino acids and the opposite surface consisting of hydrophobic (or lipophilic) ones.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
